GRUB config and validation
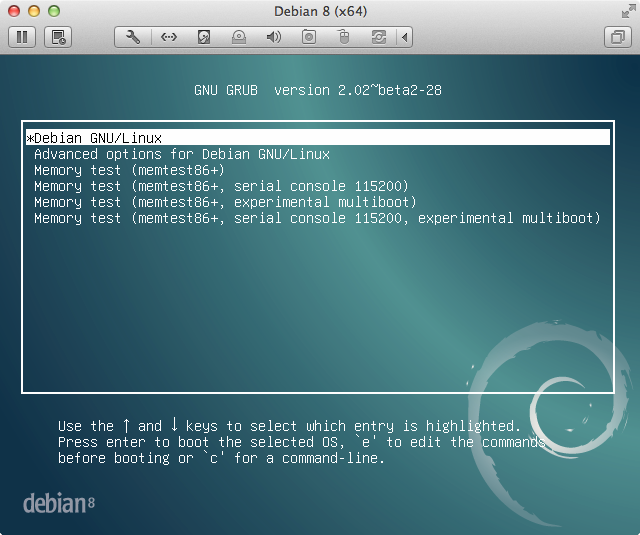
To check the GRUB settings on a Linux system, you can use the cat command to view the contents of the /etc/default/grub file. This file contains the default GRUB settings for your system.
Here's how to check the GRUB settings:
Open a terminal window on your Linux system.
Type the following command and press Enter:
cat /etc/default/grub
- The
catcommand will display the contents of the/etc/default/grubfile, which contains the default GRUB settings. You can look for settings such asGRUB_DEFAULT,GRUB_TIMEOUT, andGRUB_CMDLINE_LINUXto see the current values.
Here's an example output from the cat command:
# If you change this file, run 'update-grub' afterwards to update
# /boot/grub/grub.cfg.
# For full documentation of the options in this file, see:
# info -f grub -n 'Simple configuration'
GRUB_DEFAULT=0
GRUB_TIMEOUT=5
GRUB_TIMEOUT_STYLE=menu
GRUB_DISTRIBUTOR=`lsb_release -i -s 2> /dev/null || echo Debian`
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet splash"
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX=""
In this example, the GRUB_DEFAULT setting is set to 0, which means that the first entry in the GRUB menu will be selected by default. The GRUB_TIMEOUT setting is set to 5, which means that the GRUB menu will be displayed for 5 seconds before the default entry is selected. The GRUB_TIMEOUT_STYLE setting is set to menu, which means that the GRUB menu will always be displayed. The GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT setting is set to "quiet splash", which adds the quiet and splash options to the kernel command line.
After making any changes to the /etc/default/grub file, you should run the update-grub command to update the GRUB configuration file (/boot/grub/grub.cfg) with your changes:
sudo update-grub
This will update the GRUB settings with the changes you made in the /etc/default/grub file.
